Description:
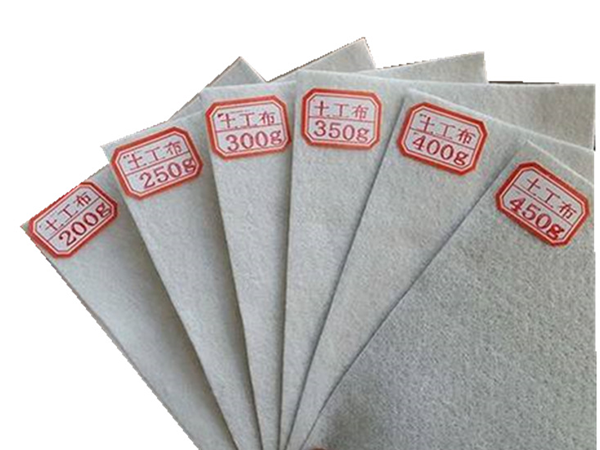
Short fiber Non woven geotextile is a new type of construction material used in civil engineering. It is made of PP or PET fibers by needle punched processes. The tensile strength of PP non woven geotextile is higher than PET non woven. But both of them has a good tear resistance and also has a good main function: filter, drainage and reinforcement. Specifications range from 100 grams per square meter to 800 grams per square meter.
Product Features:
It is an environmentally friendly building material.
Good mechanical properties, good water permeability, corrosion resistance and aging resistance.
Strong anti-burial and anti-corrosion performance, fluffy structure and good drainage performance.
Good friction coefficient and tensile strength, and has geotechnical reinforcement performance.
Good overall continuity, light weight and convenient construction.
It is a pervious material, so it has good filtering and isolation function and strong puncture resistance,so it has good protection performance.
Technical data sheet:
Mechanical Properties | weight | g/m2 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 600 | 800 |
weight variation | % | -8 | -8 | -8 | -8 | -7 | -7 | -7 | -7 | -6 | -6 | -6 | |
thickness | mm | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 5 | |
width variation | % | -0.5 | |||||||||||
Break Strength(M D adn XMD) | kN/m | 2.5 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 8 | 9.5 | 11 | 12.5 | 14 | 16 | 19 | 25 | |
Break Elongation | % | 25-100 | |||||||||||
CBR Burst Strength≥ | kN | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 3.2 | 4 | |
Tear Strength≥ (MD and XMD) | kN | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.5 | 0.6 | |
MD=Machine Direction Strength CD=Cross Machine Direction Strength | |||||||||||||
Hydraulic Prooerlies | sieve size 090 | mm | 0.07 ~0.20 | ||||||||||
Coefficient of Pemeability | cm/s | (1.0-9.9)X(10-1 ~10-3) | |||||||||||
Application:
To reinforce the backfill of retaining wall or to anchor the face plate of retaining wall. Build wrapped retaining walls or abutments.
Reinforcing flexible pavement, repairing cracks on the road and preventing reflective cracks on the road surface.
Increasing the stability of gravel slope and reinforced soil to prevent soil erosion and freezing damage at low temperature.
The isolation layer between ballast and roadbed or between roadbed and soft ground.
The isolation layer between artificial fill, rockfill or material field and foundation, and between different frozen soil layers. Filtration and reinforcement.
The filter layer of the upper reaches of the initial ash storage dam or tailings dam, and the filter layer of the drainage system in the backfill of the retaining wall.
The filter layer around the drainage pipe or gravel drainage ditch.
The filters of water wells, relief wells or oblique pressure pipes in hydraulic engineering.
Geotextile isolation layer between highways, airports.
Vertical or horizontal drainage within the earth dam, buried in the soil to dissipate the pore water pressure.
Drainage behind impervious geomembrane or under concrete cover in earth dams or embankments.